| Definitions | Methodology | Publications | Links | Contact |
Active substance – any substance or mixture of substances intended to be used in the manufacture of the medicinal product and that, when used in the production of a drug, becomes an active ingredient of the medicinal product. Such substances are intended to furnish pharmacological activity or other direct effect in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease or to affect the structure and function of the body.
ATC classification – is the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical classification system elaborated by the World Health Organization (WHO), where the active substances and their combinations are divided into different groups according to the organ or system on which they act and their therapeutic, pharmacological and chemical properties. The classification contains 14 main ATC groups with different subgroups. The more detailed information about the classifications is available on the following website: www.whocc.no. The drug consumption data for previous years are represented according to the latest version of the ATC classification. The data for 2020–2024 is represented according to the 2025 ATC classification.
DDD/1000 inhabitants/day – a number of defined daily doses per thousand inhabitants per day. Drug consumption data expressed in this way may provide a rough estimate of the proportion of the population within a defined area treated daily with certain drugs. An estimated drug consumption of 10 DDD/1000 inhabitants/day corresponds to a daily use of this drug by 1 % of the population. The DDD/1000 inhabitants/day provide a fixed unit of measurement independent of price and dosage form (e.g. tablet strength) enabling the researcher to assess trends in drug consumption and to perform comparisons between population groups.
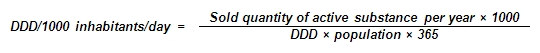
Defined Daily Dose (DDD) – the assumed average maintenance dose per day for a drug used for its main indications in adults. The defined daily dose is a unit of measurement and does not necessarily reflect the recommended or real dose. The DDD of a drug can be very difficult to establish, as the drug dose depends on indications, individuals and therapeutic practices.
Population – the population of Estonia at the beginning of a year according to Statistics Estonia.
Sold quantity of active substance per year – the volume of sales to general and hospital pharmacies and other institutions (mainly state and scientific institutions) by medicinal products sold by Estonian wholesalers during a year.
The purpose of drug consumption statistics is to improve quality of drug use and have regular, continuous and internationally comparable updates of drug consumption.
The drug consumption data are based on the sales to general and hospital pharmacies and other institutions (mainly state- and scientific institutions) by Estonian wholesalers. The calculations are based on the volume of sales, on the defined daily dose per day for each drug and the population figure at the beginning of each year.
The drug consumption statistics are expressed according to the ATC classification as the number of DDDs per thousand inhabitants per day (DDD/1000 inhabitants/day). The tables do not contain drug consumption data for several important drug groups (antineoplastic drugs, anesthetics, dermatological and ophthalmological preparations) since the DDD is not applicable. The reasons may be individual dosage, one-time usage or different routes of administration.
The drug consumption data include only medicines for human use. The classification of substances as a medicine or non-medicine is based on the Medicinal Products Act. One substance may occur as a medicine as well as a non-medicine, depending on the characteristics of the preparation. This is relevant mainly when interpreting the consumption data of vitamins (A11) and mineral supplements (A12), where the preparations classified as medicine do not represent the whole consumption of vitamins or mineral supplements as some preparations are classified as non-medicines. The data represent only preparations that are classified as medicinal products at present (year 2025). For example if a preparation that was classified as a medicine in 2023, but in 2025 is a non-medication does not occur in tables as consumption cannot be compared.
Statistical Yearbook of the State Agency of Medicines 2023. Tartu: State Agency of Medicines; 2024. Publication in pdf-format
Statistical Yearbook of the State Agency of Medicines 2023. Tartu: State Agency of Medicines; 2023. Publication in pdf-format
Statistical Yearbook of the State Agency of Medicines 2022. Tartu: State Agency of Medicines; 2022. Publication in pdf-format
More info about Statistics on medicines on State Agency of Medicines web page
WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology
State Agency of Medicines
E-mail: info[at]ravimiamet.ee
Phone: +372 737 4140
Updated: 14.05.2025