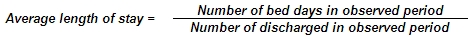
| Definitions | Methodology | Classifications | Contact |
Age group — in the statistics of hospital and day care beds, data is collected on persons aged 0-14 and persons aged 15 and older.
Annual average population — half the sum number of the population at the beginning and the end of the year. Annual average population is used for calculating rates.
Average length of stay — in case of bed specialty: average number of bed-days of all discharged in-patient patients (including deceased and transferred to another hospital) within the observed period, not depending on the cause of hospital care. Published in terms of days. In the case of intensive care beds, the number of patients transferred to other departments is added to the number of discharged in-patient patients.
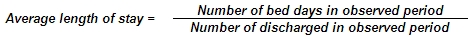
Average (annual) number of hospital beds (also see hospital bed and day care bed) — average number of hospital beds during a certain period, which have been available for the admission of a patient.
Bed day — in case of in-patient care, 24 hours, within which the admitted patient has received treatment. The day of admission and the day of discharge are considered as one day.
Bed occupancy — the average number of days in the observed period during which the hospital bed is in use.
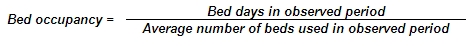
Bed occupancy rate — number of days when a hospital bed was used as a percentage of all days in the observed period.
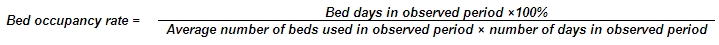
Bed turnover — average number of patients per hospital bed. In the formula, those having been in hospital is equal to the half-sum of hospitalised and discharged. Intensive care bed is an exception. In case of these beds those moved to another ward within the same hospital are included in the number of discharged and those brought from another ward of the same hospital are included in the number of hospitalised.
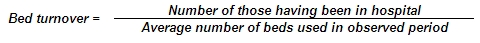
Calendar adjustment of a time series — a process of determining and elimination of the calendar component.
Calendar component — the part of seasonal component which is related to the calendar used in the country: fixed and moving holidays, leap years and other calendar-related phenomena.
County — location of health care service provider. It is classified according to the Classification of Administrative and Settlement Units of Estonia (EHAK) (see classifications). Until 2017, data by the counties is distributed by the administrative division that existed before administrative reform (October 2017). Data starting from 2018 is distributed by new administrative division.
Day care bed — bed for providing day care services.
Health care service — activities of health care personnel (doctor, dentist, nurse, midwife), the aim of which is to prevent, diagnose and treat an illness, injury or poisoning in order to alleviate people's discomfort, prevent the deterioration of his/her condition of health or to restore his/her health.
Health care services are divided into three types: out-patient health care service, or out-patient care, day care and in-patient health care service, or hospital care.Hospital — a health care provider which complies with the requirements related to location, construction, administrative organisation and staff, aimed at providing 24-hour care in medical specialities. As a rule, in addition to in-patient health care, hospitals also provide out-patient and day care.
Hospital admission — hospitalisation of a patient in an in-patient facility, involving a stay of at least 24 hours (admitted patient).
Hospital bed (also in-patient bed) — a bed which is meant for 24-hour provision of a health care service at the hospital. The number of hospital beds is published as of the end of the period (quarter, year).
Hospital bed speciality — determined through the health care services provided in connection with the hospital bed. The list of specialities is introduced with the legal acts regulating the health care system of the country. Hospital beds are divided into curative (acute) care and long-term care beds.
Hospital discharges by the speciality of hospital beds — total number of patients discharged from hospitals during a certain period (a calendar year, a quarter), including the deceased or transferred to another hospital.
Hospital included in the Hospital Network Development Plan — Hospital Network Development Plan, prescribed by the Government of the Republic Regulation No 105 of 2 April 2003, includes 3 regional hospitals, 4 central hospitals, 11 general hospitals, 1 local hospital and 1 rehabilitation hospital.
Inhabitant of another county — a person admitted to the hospital whose permanent place of residence is not in the same county as the hospital. The hospital located in Tallinn indicates a patient admitted from Harju County as an inhabitant of another county and vice versa.
Legal form — the form of existence of persons, agencies and organisations and other legal subjects specified in the legislation of the Republic of Estonia. The legal forms include: self employed person, private limited company, public limited company, foundation and other legal forms (general partnership, limited partnership, commercial association, a branch of a foreign company, non-profit association, state entity, local government entity) (see classifications).
Rate per 100 000 inhabitants (in case of hospital beds) — the number of hospital beds per year per 100 000 inhabitants. The number of inhabitants is considered as at 1st of January of the following year. In case of number of bed days, hospital admissions or hospital discharges rate per 100 000 inhabitants is calculated using annual average population.
Seasonal adjustment of a time series — a process of determining and elimination of the seasonal component. Seasonality can be caused by natural factors, administrative conditions, and social and cultural traditions.
Seasonal component — the part of the variations in a time series representing intra-year fluctuations that are more or less stable year after year with respect to timing, direction and magnitude.
Type of hospital — seven types of hospitals are distinguished on the basis of provided health care services: regional hospital, central hospital, general hospital, local hospital, special hospital, rehabilitation hospital and nursing care hospital. The local hospital was introduced in 2003 (see classifications).
Type of owner — shows the ownership of an establishment either by the public sector (the capital share of the state and/or local government is 50% or more) or the private sector (the capital share of an Estonian private body and/or foreign private body is 50% or more) (see classifications).
The aim of collection of data about hospital beds and day care beds is to get an overview of health care system resources and their utilization.
The data are collected in accordance with the Health Care Services Organisation Act (HCSOA) and Decree No. 51 "Health Care Statistics and the Requirements for Preparation of Economic Activity Reports in the Area of Health Care, the Composition of Data and the Procedure for Submission" (in Estonian), issued on 7th December 2013, by the Minister of Social Affairs on the basis of the HCSOA.
Every year, all in-patient health care providers are required to submit a report "Hospital (until 2018 for each month report “Hospital beds and hospitalization“). The data about the number of day care beds is collected from all day care providers by the annual report “Day Care“.
The data are published in absolute numbers and in rates per 100 000 inhabitants.
About seasonal correction (hospital beds' data for 2003–2016)
Seasonal correction of a timeline is the process of determining and elimination of the seasonal component. Seasonality can be caused by natural factors, administrative conditions, and social and cultural traditions.
Seasonal adjustment enables comparisons between time periods and interpreting the development of the series with different seasonal patterns. Seasonal adjustment is important when observing changes in two conterminous periods (month/ quarter), because two periods that follow each other directly are usually characterized by strong seasonality. Only tendencies of slope and their expansion rate can be described when we talk about seasonally adjusted time series. The number of one element of adjusted time series does not characterize reality nor does it represent a real number. Thus, when comparing the same period of two different years, it is suggested to use seasonally unadjusted data.
For seasonal adjustment of time series Eurostat's free software DEMETRA 2.04 and its integrated model TRAMO/SEATS that is based on parametric methods is used. The model is updated once a year on average. The parameters of time series are updated retroactively for 4 years since last observation. Additional information about seasonal adjustment can be found here (in Estonian).
Classification of Administrative and Settlement Units of Estonia (EHAK)
This classification is used upon submission of regional statistics. Regional health care statistics are submitted by 15 counties. Information about Tallinn and Tartu is submitted separately. Until 2017, data by the counties is distributed by the administrative division that existed before administrative reform (October 2017). Data starting from 2018 is distributed by new administrative division. This classification system is available on the webpage of the Statistics Estonia (in Estonian) in the Classifications section.
Classification of hospitals
On the basis of the services they provide hospitals are divided into seven types: regional hospitals, central hospitals, general hospitals, local hospitals, special hospitals, rehabilitation hospitals and nursing care hospitals. Requirements for different hospital types are laid down in Decree No. 103 "Requirements for Hospital Types" (in Estonian), issued by the Minister of Social Affairs on 19 August 2004.
Type of owner
Type of owner serves as the basis for the classification of health care service providers according to whether they belong to state or private sector. This classification system is available on the webpage of the Statistics Estonia (in Estonian) in the Classifications section.
Classification of legal forms
Classification of legal forms is used for the classification of health care service providers on the basis of the legal form. This classification system is available on the webpage of the Statistics Estonia (in Estonian) in the Classifications section.
Classification of bed specialities
Bed specialities are determined by the health care services offered in relation with particular in-patient beds. These specilities are set by the laws that regulate national health care system.
New classification of bed specialities was enforced on the 1st of January 2013. This bases on the Estonian E-Health classification. Below, there is a transition table for current and previous version of the classifications.
In the database, statistics of the hospital beds is presented as follows:
1) Table No RV222 (quarterly statistics), RV30, RV40 – according to the previous (until 31.12.2012) classification for the period 2003—2012;
2) Table No RV2221 (quarterly statistics), RV301, RV401 – according to the current classification for the period 2003 onwards.
| Bed speciality since 01.01.2013 | Bed speciality until 31.12.2012 | |
| 1 | acute psychiatrics | acute psychiatrics |
| 2 | endocrinology | endocrinology |
| 3 | gastroenterology | gastroenterology |
| 4 | gynecology | gynecology |
| 5 | haematology | haematology |
| 6 | nursing care | nursing care |
| 7 | intensive care, level I | adults’ intensive care, level I + children’s intensive care, level I |
| 8 | intensive care, level II | adults’ intensive care, level II + children’s intensive care, level II |
| 9 | intensive care, level III | adults’ intensive care, level II + children’s intensive care, level II |
| 10 | cardiac surgery | cardiac surgery |
| 11 | cardiology | cardiology |
| 12 | occupational diseases | - |
| 13 | otorhinolaryngology | Adults’ otorhinolaryngology + children’s otorhinolaryngology |
| 14 | pediatrics | pediatrics |
| 15 | children’s surgery | children’s surgery |
| 16 | children’s neurology | children’s neurology |
| 17 | children’s psychiatrics | children’s psychiatrics |
| 18 | dermato/venereal diseases | adults’ beds for dermato/venereal diseases + children’s beds for dermato/venereal diseases |
| 19 | infectious diseases | infectious diseases beds for adults + infectious diseases beds for children |
| 20 | nephrology | nephrology |
| 21 | neurosurgery | neurosurgery |
| 22 | neurology | adults’ neurology + children’s neurology |
| 23 | orthognathic surgery (dental and oral surgery) | orthognathic surgery (dental and oral surgery) |
| 24 | oncology | oncology |
| 25 | orthopaedics | adults’ orthopaedics for adults + children’s orthopaedics |
| 26 | psychiatrics | psychiatrics |
| 27 | pulmonology | pulmonology |
| 28 | burns | burns |
| 29 | radiology | radiology |
| 30 | pregnancy pathology | pregnancy pathology |
| 31 | rheumatology | rheumatology |
| 32 | thoracic surgery | thoracic surgery |
| 33 | ophthalmology | ophthalmology |
| 34 | internal medicine | internal medicine |
| 35 | obstetrics | obstetrics |
| 36 | rehabilitative care | rehabilitative care |
| 37 | traumatology | adults’ traumatology + children’s traumatology |
| 38 | tuberculosis | tuberculosis |
| 39 | urology | urology |
| 40 | vascular surgery | vascular surgery |
| 41 | general surgery | general surgery |
Katrin Tomson
Department of Health Statistics
National Institute for Health Development
E-mail: Katrin.Tomson[ät]tai.ee
Updated: 5.10.2022