| Definitions | Methodology | Classifications and lists | Publications | Contact |
Acute care hospital — according to type of hospitals in Estonia: regional, central, general, local, special and rehabilitation hospitals. Includes nursing care in acute care hospitals. Excludes nursing care hospital.
Age group — in the statistics of hospital and day care discharges, data is collected on persons aged 0-14 and persons aged 15 and older or by 5-year age groups.
Average length of stay (ALOS) — average number of bed days of all in-patient patients discharged from a certain hospital within a year according to the reason for hospital care. Presented in terms of days.
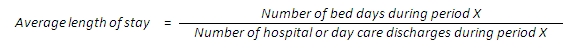
Average length of stay (in hospital care, with deceased) — average number of bed days of all in-patient patients discharged (with deceased) from hospital within a year according to the diagnosis. ALOS is calculated by dividing the number of days stayed by the number of discharges (with deceased). Number of days equals date of discharge minus date of admission.
Average length of stay (in hospital care, without deceased) — average number of bed days of all in-patient patients discharged (without deceased) from hospital within a year according to the diagnosis. ALOS is calculated by dividing the number of days stayed by the number of discharges (without deceased). Number of days equals date of discharge minus date of admission.
Average length of stay (in day care) — average number of bed days of all day care patients discharged within a year according to the reason for day care. ALOS is calculated by dividing the number of days stayed by the number of discharges. All days are counted. Hemodialysis is counted to one case in year for each patient.
County — location of health care service provider (tables PH02, PH1, PH2 and PH3) or patient’s permanent place of residence (table PH5). It is classified according to the Classification of Administrative and Settlement Units of Estonia (EHAK) (see classifications and lists). Until 2017, data by the counties is distributed by the administrative division that existed before administrative reform (October 2017). Data starting from 2018 is distributed by new administrative division.
Disease group — disease group presented according to the international statistical classification of diseases and health problems (ICD-10) (see classifications and lists).
Health care provider or health care facility — a legal person who's principal or ancillary activity is to provide health care services. Health care providers must have an activity licence issued by the Health Board (Health Care Board until 1 January 2010).
Health care service — activities of health care personnel (doctor, dentist, nurse, midwife), aimed at preventing, diagnosing or curing a disease, an injury or poisoning, at alleviating human suffering, at preventing the state of health of a patient from worsening or exacerbating and at improving the patient’s health.
Health care services are divided into three types: outpatient health care service, or outpatient care, day care and in-patient health care service, or hospital care.
Hospital or day care discharges by diagnosis (without deceased) — total number of patients discharged during the given calendar year excl. transferred to another hospital, died or proved healthy.
Hospital or day care discharges by diagnosis (with deceased) — total number of patients discharged during the given calendar year by principal diagnosis. Deceased patients are included, persons who were transferred to another hospital or were proved to be healthy after examination are excluded. Stillborns are excluded.
ICD-10 — International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision (see classifications and litsts).
Live birth — delivery of a child showing evidence of life (breathing, heartbeat, pulsation of the umbilical cord or definite movement of voluntary muscles) irrespective of the duration of pregnancy.
Principal diagnosis — the main reason the patient is treated. Coded by ICD-10 (see classifications and lists).
Stillbirth or late foetal death — intra-uterine death of the foetus weighing at least 500 grams at birth, which took place after the 22nd week of pregnancy.
Type of care — data by type of care is collected from 2016. The type of care is divided in reasons for treatment tables (PH01, PH1, PH02 and PH2) as follows:
The purpose of collecting statistics on the reasons for hospital and day care is to assess the reasons and durations of the need for hospital or day care.
The data are collected from facilities that have been issued activity licences for the provision of health care services, pursuant to the Health Care Services Organisation Act and decree by the Minister of Social Affairs.
The data on the reasons for hospital care are collected with the “Hospital” report. Reporting is mandatory for all legal persons that have provide in-patient health care services (HP.2 nursing care hospitals are included) during calendar year. The data on the reasons for day care are collected with the “Day Care” report. Reporting is mandatory for all legal persons that have provide day care services during calendar year.
Health care providers submit the data according to their location.
Data are presented according to the tenth revision of the international statistical classification of diseases and health problems (ICD-10).
Classification of Administrative and Settlement Units of Estonia (EHAK)
This classification is used upon submission of regional statistics. Regional health care statistics are submitted by 15 counties. Information about Tallinn and Tartu is submitted separately. Until 2017, data by the counties is distributed by the administrative division that existed before administrative reform (October 2017). Data starting from 2018 is distributed by new administrative division. This classification system is available on the webpage of the Statistics Estonia in the Classifications section.
The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision (ICD-10)
This classification is used to code diagnoses and submit the data about disease cases in accordance with the diagnoses. The classification system is available on the webpage of the World Health Organization.
National Institute for Health Development of Estonia, The National Health Service of Latvia, Health Information Centre, Institute of Hygiene, Lithuania. Health in the Baltic Countries 2016. Tallinn: National Institute for Health Development; 2018. Report in pdf-format
Merike Rätsep
Department of Health Statistics
National Institute for Health Development
E-mail: Merike.Ratsep[at]tai.ee
Updated: 13.10.2022