| Definitions | Methodology | Classifications | Contact |
Age group – in health care statistics a child is considered to be a person aged 0–14 years, while an adult is a person aged 15 years and older.
All involuntarily hospitalised – number of persons hospitalised according to the § 11 involuntary emergency psychiatric care of the Mental Health Act in the reference year.
Annual average population – half the sum number of the population at the beginning and at the end of the year. This index is used to calculate rates.
Average length of stay (ALOS) – average number of bed-days of all patients checked out from hospital within a year according to the reason for hospital care. Presented in terms of days.
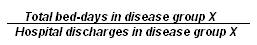
Bed day – in case of inpatient care, 24 hours, within which the admitted patient has received treatment. The day of admission and the day of discharge are considered as one day. The bed day for day care is equal to the number of times the day care service is provided to the patient.
Diagnosis (according to ICD-10) – the diagnosis established according to the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD-10). Mental and behavioural disorders are classified in the chapter V of the ICD-10 (codes F00–F99).
Directed to coercive treatment by court – number of persons hospitalised according to the § 86 Coercive psychiatric treatment of the Penal Code in the reference year.
Health care provider or health care facility – a legal person whose principal or ancillary activity is to provide health care service. Health care provider must have an activity licence issued by the Health Board (Health Care Board until 1 January 2010).
Health care service – activities of health care personnel (doctor, dentist, nurse, midwife), aimed at preventing, diagnosing or curing a disease, an injury or poisoning, at alleviating human suffering, at preventing the state of health of a patient from worsening or exacerbating and at improving the patient’s health. Health care services are divided into three types: outpatient health care service, or outpatient care, day care and inpatient health care service, or hospital care.
Hospital admission – hospitalisation of a patient in an inpatient facility, involving a stay of at least for 24 hours (admitted patient).
Hospital or day care checkouts – the number of patients checked out from hospital or day care during the given calendar year. Deceased patients, persons who were transferred to another hospital or were deemed to be healthy are excluded.
ICD-10 – International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision (see Classifications).
Incidence rate – denotes the number of new cases of a disease in relation to the size of the population during a certain period of time. As a rule, this index is calculated per 100,000 inhabitants per year. Sex and age rates are also used.
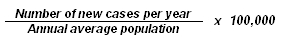
Incidence or new case of a disease or new case – the final diagnosis confirmed for the first time in the life of a patient.
Outpatient care patient – a person who received outpatient counselling or treatment. The total number of consulted patients includes both new and prevalent cases.
Psychiatric patient – the patient diagnosed with a mental or behavioural disorder by psychiatrist.
Principal diagnosis – the main reason the patient is treated. Coded according to ICD-10 (see Classifications).
Psychoactive substance – psychoactive substances are substances which affect psychical functions and can cause addiction, such as alcohol, opiates (e.g. heroin, morphine), cocaine and other stimulants, hallucinogens, nicotine and volatile substances.
The aim of the statistics for mental and behavioural disorders is to give information about the occurrence of mental and behavioural disorders among the persons in outpatient, day care and inpatient psychiatric treatment and according to that evaluate the prevalence of mental and behavioural disorders in the population.
The data on mental and behavioural disorders is collected using the annual report “Mental and Behavioural Disorders”. This report must be submitted by all psychiatric care service providers which hold a relevant activity licence and which employ psychiatrist(s). The service providers submit reports through web-based data submission environment A-veeb. The data collection is legally defined in accordance with the Health Care Services Organisation Act (HCSOA) and decree by the Minister of Social Affairs on the basis of the HCSOA.
The reports include cases diagnosed by psychiatrists. Therefore, they do not include data about the cases diagnosed by family doctors, etc. Information about mental and behavioural disorders diagnosed by psychiatrists is submitted in an aggregated form by disease groups and diagnosis according to ICD-10. The data related to inpatient care and day care is distinguished from the data related to outpatient care.
Mental and behavioural disorders statistics is published in absolute or relative numbers (rate per 100,000 inhabitants using annual average population).
The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision (ICD-10)
This classification is used to code diagnoses and submit the data about disease cases in accordance with the diagnoses. The classification system is available on the webpage of the World Health Organization.
Reet Nestor
Department of Health Statistics
National Institute for Health Development
E-mail: Reet.Nestor[at]tai.ee
Updated: 30.07.2021