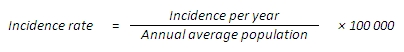
| Definitions | Methodology | Data visualization | Classifications and lists | Contacts |
Actions at the time of the occurrence of the incident — actions which resulted in the injury or poisoning of the patient. They are codified on the basis of Chapter XX: External causes, code 5 of ICD-10 (0–4, 8, 9) (see methodology).
Average annual population — half the sum number of the population at the beginning and the end of the year. This index is used to calculate rates.
Birth weight — the first weight of the fetus or newborn obtained after birth (preferably measured within the first hour of life).
County — place of residence in tables EH02 and EH04, location of health care service provider in table EH11. It is classified according to the Classification of Administrative and Settlement Units of Estonia (EHAK) (see classifications and lists).
Diagnosis (according to ICD-10) — The diagnosis established according to the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD-10).
External causes of injuries and poisonings — outer environmental factors, events and circumstances which have caused the injury or poisoning. External causes are classified on the basis of Chapter XX (V01–Y98) of ICD-10.
Health care provider or health care facility — a legal person whose principal or ancillary activity is to provide health care services. Health care provider must have an activity licence issued by the Health Board (Health Care Board until 1 January 2010).
Health care service — activities of health care personnel (doctor, dentist, nurse, midwife), aimed at preventing, diagnosing or curing a disease, an injury or poisoning, at alleviating human suffering, at preventing the state of health of a patient from worsening or exacerbating and at improving the patient’s health. Health care services are divided into three types: outpatient health care service, or outpatient care, day care and inpatient health care service, or hospital care.
ICD-10 — International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision.
Incidence — occurrence of new cases of a specified disease among the population during a specified period of time. It can be measured by the absolute number, which means the number of new cases of disease during a specified period of time, or the relative number, which means the disease occurrence rate (i.e. incidence rate), denoting the number of new cases of a disease in relation to the size of the population during a certain period of time. In health statistics: incidence registered by service providers.
Incidence rate — denotes the number of new cases (the final diagnosis confirmed for the first time in the life of a patient) of a disease in relation to the size of the population during a certain period of time. As a rule, this index is calculated per 100 000 people per year considering sex and age rates.
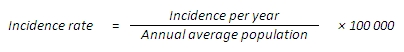
Live birth — delivery of a child showing evidence of life (breathing, heartbeat, pulsation of the umbilical cord or definite movement of voluntary muscles) irrespective of the duration of pregnancy.
New case of a disease or a new case — the final diagnosis confirmed for the first time in the life of a patient.
Newborn — child from birth to 4 weeks of age.
Place of residence — the patient's place of residence at the county level according to the population register at the time of health care service provision (opening of treatment claim). Classified according to the Estonian administrative and settlement division classifier (EHAK) (see classifications and lists). A separate category is provided for a residence outside Estonia, unknown county and unknown place of residence. The unknown county is counted under Estonia. If the place of residence is outside Estonia or unknown, cases of illness are not counted under Estonia.
Stillbirth or late fetal death — intra-uterine death of the fetus weighing at least 500 grams at birth, which took place after the 22nd week of pregnancy.
Treatment claim — an invoice for treatment costs presented by a health care provider to the Estonian Health Insurance Fund for services provided to a patient.
The aim of collecting morbidity statistics is to get regular national overviews of the rate of morbidity of the population, to compare the data concerning the morbidity and to ensure its consistency.
The data is submitted on the basis of 10th Revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems classification (ICD-10): Ch. I–XIX (codes A00–R99), excluding malignant neoplasms (Ch. II, codes C00–C97). Morbidity statistics on malignant neoplasms is available under the topic "Malignant neoplasms" and injuries statistics is available under the topic "Injuries" in the Morbidity subdivision of the Health Statistics and Health Research Database.
Estimated incidence
Since 2021, incidence is calculated based on treatment claims submitted to the Health Insurance Fund. Time series are published retrospectively from 2016.
All treatment claims submitted to the Estonian Health Insurance Fund from 2013 are included, covering both insured and uninsured Estonians and residents of Estonia. Treatment claims do not reflect contacts with the health care system if a person has visited a health care provider that does not have a treatment financing contract with the Estonian Health Insurance Fund, or if the health care provider is a Estonian Health Insurance Fund contract partner but the person paid for the service in full themselves. Diagnoses registered in prisons and the Estonian Defence Forces are also not reflected on treatment claims.
In the case of chronic diseases, a case is considered a primary case if the person has not been diagnosed with the same disease in the previous 7 years. Since treatment claims from 2013 onwards are used for statistics, in cases with a look-back period shorter than 7 years, the number of primary cases found from treatment claims is adjusted to correspond conditionally to a 7-year look-back period.
The incidence found based on the new methodology is not comparable with the statistics published until 2016 (tables EH10–EH12). Previously, the data underlying the incidence statistics were aggregated, not individual-based. Therefore, multiple counting of a single case could not be avoided, and the previously published statistics are likely overestimated. Based on the treatment claims submitted to the Estonian Health Insurance Fund, it can be said that depending on the disease, the overestimation of initial cases in the previous statistics can reach several tens of percent.
When using the data, it should be remembered that it is an estimate. Special attention should be paid to interpreting very small numbers. In cases of a very small number of cases or a small population, random fluctuations significantly affect the calculated incidence rate. For example, if one incidence case is diagnosed in Hiiu county in the age group 0–14, then we could see the highest incidence rate in Estonia for Hiiu county.
Registered incidence until 2016
The data is collected from all institutions providing health care services which hold a relevant activity licence and from family physicians working with practice lists in accordance with the Health Care Services Organisation Act (HCSOA) and decree by the Minister of Social Affairs on the basis of the HCSOA.
The data about registered incidence was presented in the annual report “Health Care Institution“. All legal persons providing outpatient and inpatient services were required to submit the report, excluding emergency medical care and dental care institutions, which submit data about their activities in other type of reports.
The data are published in absolute and relative numbers (rate per 100 000 inhabitants; incidence rate of newborns is calculated per 1000 live births). The number of live births in Estonia registered by the Estonian Medical Birth Registry serves as the basis for calculation of the incidence rate of newborns. The incidence rate of newborns includes the incidence of all newborns born in Estonia (including those whose residence is abroad).
Morbidity statistics concerning registered incidence must be submitted by health care service providers. Health care service providers are required to submit data according to the registered location of activities of their undertaking, which is why the county division of the morbidity data is based on the location of the health care service provider, not on the place of residence of the patient.
Due to the preparations for the transfer to statistics based on individual data every doctor must from 2005 onwards register only the new cases diagnosed by them personally. Earlier the new diagnoses given in hospitals were registered by the patient's family doctor. The arrangement process for case registration system has differed by institutions and this causes annual fluctuations, for example, due to double registration.
Newborn health problems, diseases and certain conditions originating in the perinatal period
Data on newborns diagnosed with health problems, diseases and certain conditions originating in the perinatal period were collected from obstetric care providers until 2020 with the annual report “Newborn's morbidity” (previously until 2012 “Pregnant women and newborns”, 2013–2015 “Pregnant women and newborn's illnesses”). Data were provided by maternity wards on cases diagnosed and registered there. The data include both primary and concomitant diagnoses and certain conditions originating in the perinatal period, excluding of Z-diagnoses.
Data were collected when the child was 7 days old or as early as the day the child leaves the hospital, is transferred to another medical institution, or dies before the age of 7 days. The exception is the Tartu University Hospital since 2015, where the treatment of a newborn with the disease takes place in another department of the same hospital already for the first 7 days, therefore not all diagnoses of children are registered in the maternity ward but also those diagnoses that is diagnosed in another ward (neonatology, children's intensive care).
In 2020, maternity care in Estonia was provided by 13 health care providers.
The basis for calculating the morbidity rate is the number of live births in the Estonian Medical Birth Register of the respective year.
When using the data, it is important to remember that several diagnosis codes may be registered in one newborn. Also, not all ICD-10 diagnostic codes always mean the presence of a serious illness, but also the registration of a complication, trauma, or minor health problem during childbirth.
For example, the most frequently registered P05-P08 diagnoses are related to the growth of the newborn - the child is either lighter or heavier due to the duration of pregnancy; or unspecified neonatal jaundice (P59), which is usually a transient condition but may be the symptom for another disease. In addition, based on the data collected as aggregated data, it is not possible to extract diagnoses in detail.
Congenital malformations, deformities and the diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities (Q00–Q99) also include ICD-10 code Q38.1 tongue tear that can be severed by a pediatrician during a simple surgical procedure. The diagnosis of perinatal conditions also includes conditions that cannot be directly considered a neonatal health problem, such as difficulties in breastfeeding a newborn (P92.5), which are more related to the maternal health condition of the mother.
From 2021, data collection is discontinued according to the report "Newborn's morbidity". The collection and publication of data continues on the basis of the information on birth cards transmitted to the medical birth register and the statistics is available under database topic "Population" - "Births and breastfed infants".
Classification of Administrative and Settlement Units of Estonia (EHAK)
This classification is used upon submission of regional statistics. Regional health care statistics are submitted by 15 counties. This classification system is available on the webpage of the Statistics Estonia in the Classifications section.
The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision (ICD-10)
This classification is used to code diagnoses and submit the data about disease cases in accordance with the diagnoses. The classification system is available on the webpage of the World Health Organization.
Jane Idavain
Department of Health Statistics
National Institute for Health Development
E-mail: Jane.Idavain[at]tai.ee
Newborn health problems and diseases' data
Eva Anderson
Department of Health Statistics
National Institute for Health Development
E-mail: Eva.Anderson[at]tai.ee
Updated: 14.11.2025