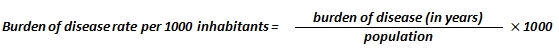
| Definitions | Methodology | Publications |
Burden of disease or time lost due to ailments measured in years per 1000 residents. This metric shows the gap between the population's actual and theoretically possible (i.e. best) health condition by calculating the sum total of years lost due to premature deaths and illnesses. Burden of disease is therefore measurable in years which an individual and the population as a whole could have used in case diseases and premature deaths would not have occurred. The aggregated figure is calculated by adding up mortality and losses due to illness.
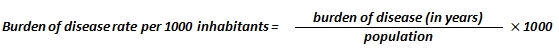
The primary causes of the loss of health in Estonia include cardiovascular diseases, injuries and tumours. The figures indicate vast disparities between different counties, reflecting gulfs between individual regions' socioeconomic conditions. The aforementioned indicators are useful when evaluating the changes that have taken place in different counties during a given timeline – i.e. indicating whether there has been an improvement or decline.
Years lived with disability per 1000 inhabitants shows the number of living years lost as a result of illness and injury. Years lived with disability is the time, measured in years, which an individual and the population as a whole could have used in case illnesses would not have occurred. The metric is calculated by multiplying the number of all cases of illnesses (that have been subdivided into categories based on gender, age, diagnosis) with a severity factor ascribed to each illness. Severest illnesses are those which result in the largest decreases in a person's quality of life and loss of working ability, potentially causing the loss of the larger part of the afflicted person's projected lifetime. Mild illnesses are those which result in an insignificant loss of health in a single year. Years lived with disability per 1000 inhabitants are calculated as following:

Years of life lost per 1000 inhabitants shows the loss of living years resulting from premature deaths. Years of life lost is the time, measured in years, which an individual and the population as a whole could have used in case premature deaths would not have occurred. A death is classified as premature in cases where it occurs earlier than the projected lifespan of a given age group. Therefore the earlier the death, the greater the years of life lost. The years of life lost figure is calculated by aggregating the differences between the actual and projected average lifespans of persons at the time of deaths taking into account their gender, age and other factors. Years of life lost rate per 1000 inhabitants in a county or municipality is calculated using the following method:
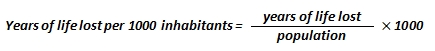
Calculations of 2006 is done by Ministry of Social Affairs.
Years of life lost by premature deaths is calculated by aggregating the differences between the actual and projected average lifespans of persons at the time of deaths taking into account their gender, age and other factors. A death is classified as premature in cases where it occurs earlier than the projected lifespan of a given age group. Therefore the earlier the death, the greater the years of life lost. Years lived with disability (YLD) is calculated by multiplying the number of all cases of illnesses (that have been subdivided into categories based on gender, age, diagnosis) with a severity factor ascribed to each illness. Severest illnesses are those which result in the largest decreases in a person's quality of life and loss of working ability causing the loss of the larger part of the afflicted person's projected lifetime, where as mild illnesses are those which result in an insignificant loss of health in a single year.
Burden of disease is calculated by aggregating years of life lost and years lived with disability figures with the combined figure expressed as "disability adjusted life years – DALY". This method carries the advantage of providing a more complete insight into the overall health of the population compared to classical statistical data by taking into account the time of death and illness severity data/indicators.
Lai T, Köhler K. Burden of Disease of Estonian Population. Policy Brief. Series of the Ministry of Social Affairs No 1/2009 eng.